Pig farming
During the rearing period, pigs face many challenges that can impact their well-being and performances with consequences on farmers’ income.
Based on its expertise in plant-active ingredients, Phytosynthese offers a range of products that help to support animals faced with these challenges.
Thanks to the diversity of vegetal active compounds, the offered solutions have a wide application scope (digestive, respiratory, behavior, metabolism, etc.) and are adapted to all physiological stages: piglets, fatteners and sows.

Piglets


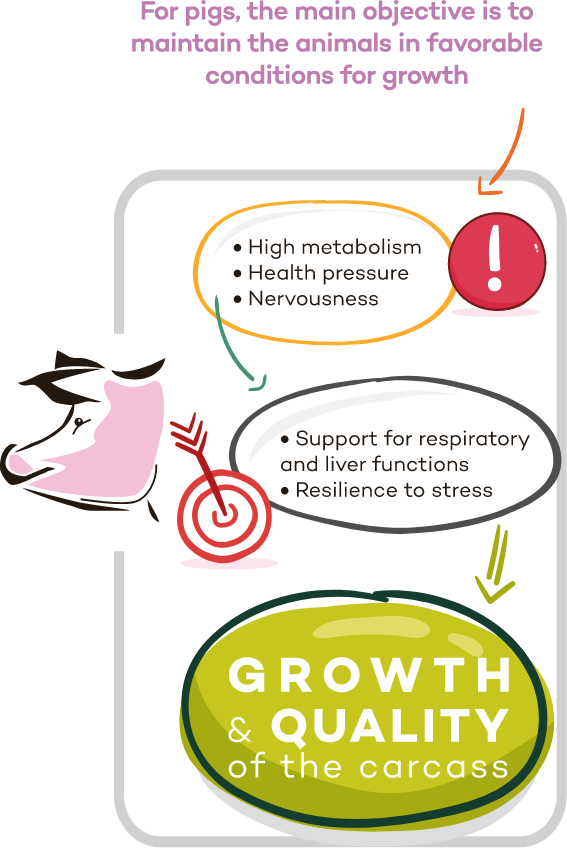
Pigs

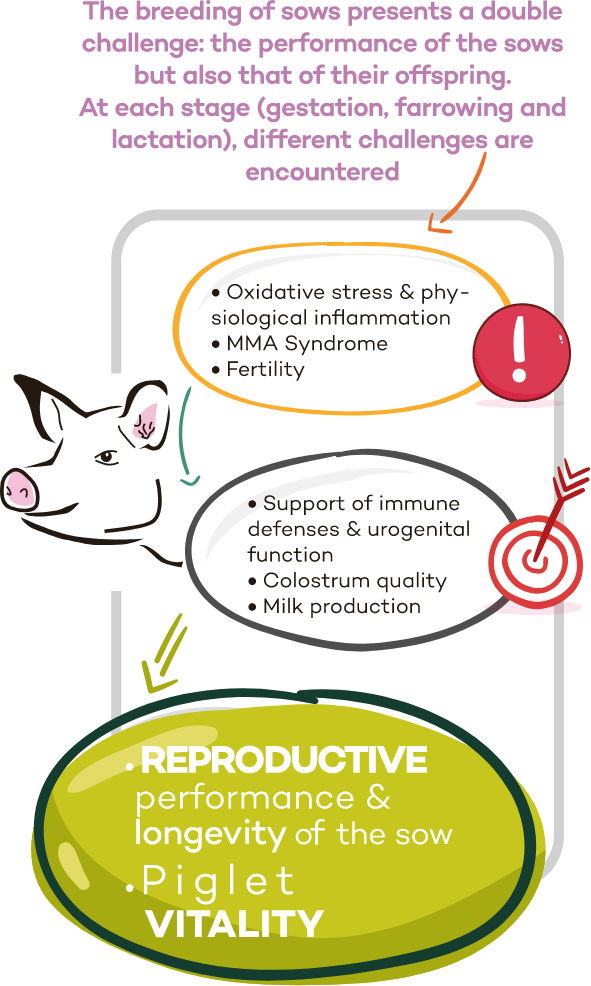
Sows
Challenges
in breeding

Digestive
Digestive disorders are a recurring issue in swine farms, in particular in piglets.
Indeed, weaning stress and immaturity of digestive and immune functions are favorable to the emergence of dysbiosis.
In fattening, digestive problems can also appear at feed transitions or in presence of pathogens (Lawsonia intracellularis, Brachyspira hyodysenteriae).
➜ These gastrointestinal problems can cause a high morbidity and economic losses for farmers.
Distribution of pathogens causing diarrhea according to affected animal category
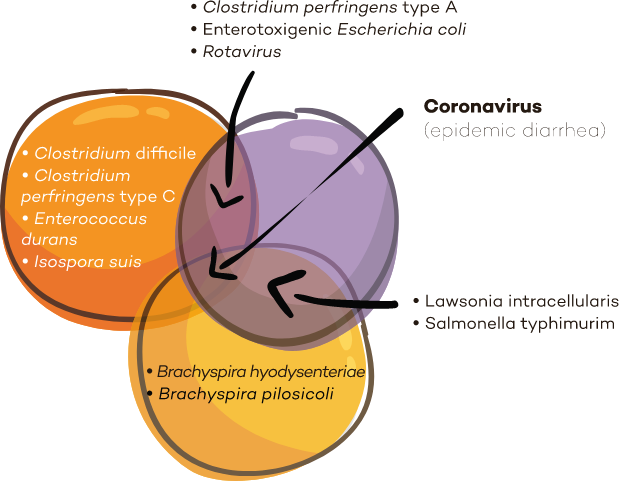
Farming diseases of pigs (GP Martineau)

Hepatic
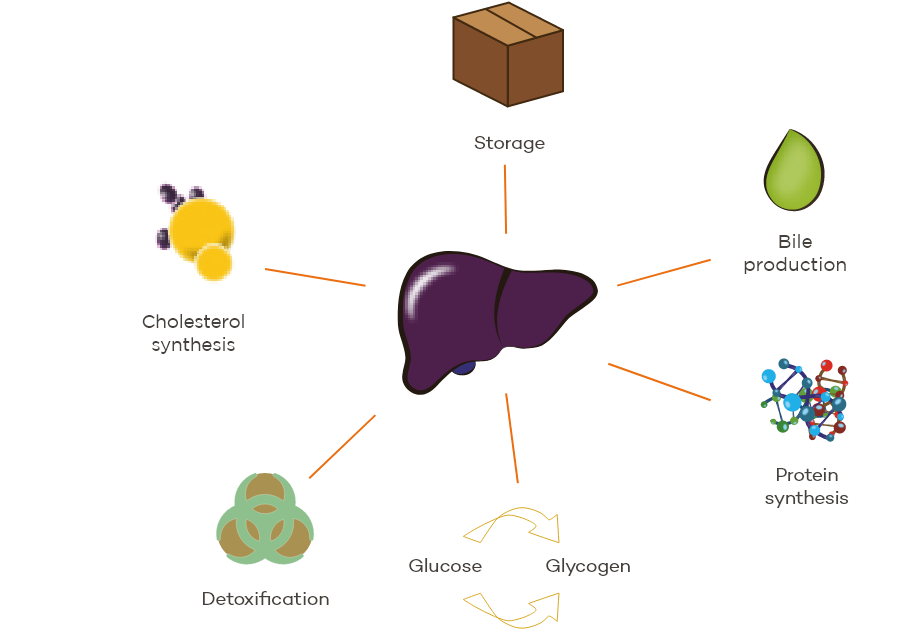
The liver ensures many functions (metabolism, storage, detoxification) essential to maintaining animal well-being and performances.
➜ Periods of high liver metabolism (growth peak, lactation) can lead to hepatic overload with consequences such as impaired feed intake and performances.

Respiratory
Respiratory disorders are frequent in swine farms, especially in fattening.
➜ Respiratory pathogens (virus, bacteria such as Actinobacilllus pleuropneumoniae, Pasteurella multocida) or poor rearing conditions (density, temperature, humidity) can weaken the respiratory tract and cause morbidity.
Mechanisms and possible consequences of viral and/or bacterial infections of the porcine respiratory tract
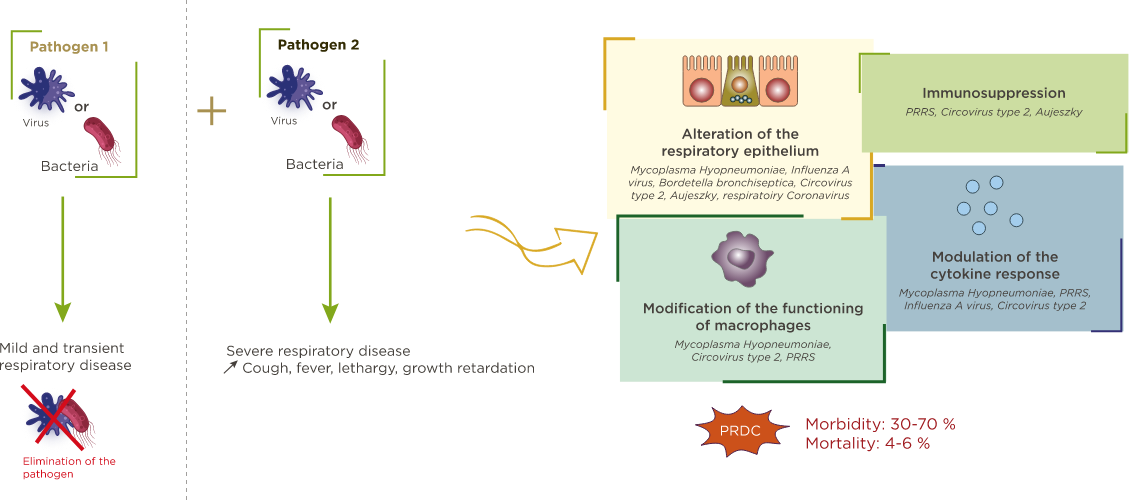
Mechanisms and possible consequences of viral and/or bacterial infections of the porcine respiratory tract (adapted from Opriessnig et al.)

Parasitic
In order to meet consumer demand, alternate farming systems (Free-range, straw bedding, quality label) are booming.
➜ These types of rearing are often subject to parasitism (Ascaris suum, Oesophagostomum dentatum) and high infestation can penalize well-being and performances: nutrient spoliation by worms, liver seizures at slaughterhouse.
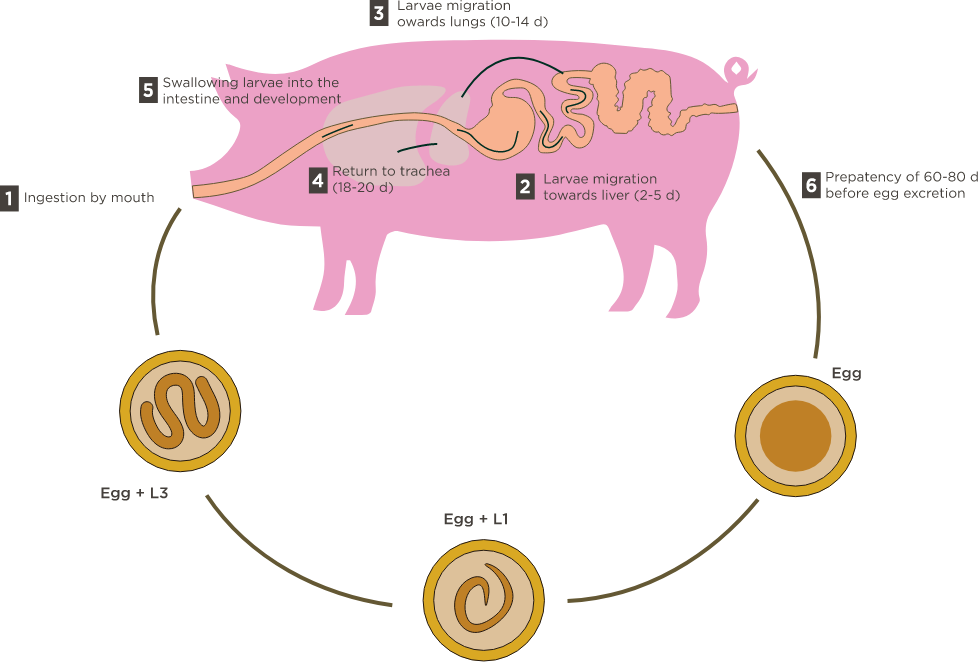
www.3trois3.com

Behavior
Weaning, farrowing, mixing of animals, transportation are sources of stress and nervousness.
➜ They generate negative behavior (cannibalism, climbing, fights) that impacts well-being but also performances.
Metabolism
During the rearing period, animals can face several stresses : physiological (weaning, farrowing), environmental (thermal) or nutritional (feed transitions).
➜ All these factors generate inflammatory reactions and oxidative stress at systemic level.
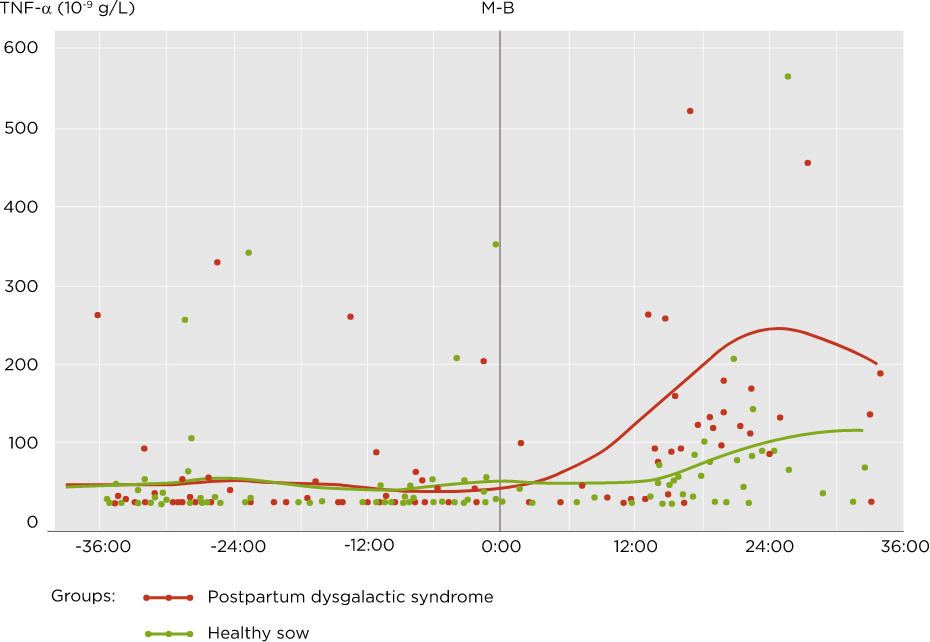
Inflammatory markers before and after farrowing in healthy sows and in sows affected with postpartum dysgalactia syndrome (Kaiser, 2018)

Urogenital
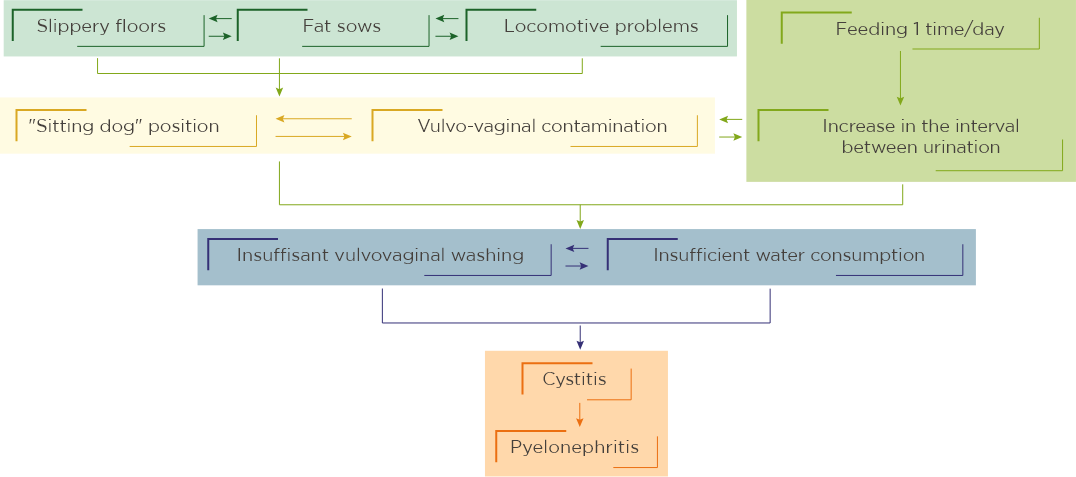
In sows, urinary disorders are very frequent, they can appear for different reasons, both physiological and morphological:
- contamination of vulva by feces;
- contamination by ground (seated position, slippery floors, locomotion problems, overweight);
- injuries of urogenital tract during farrowing.
www.3trois3.com
